Author: Zishan Haider
Gabriel's Law Blog
Introduction
“Law” is one of the 21 established disciplines of knowledge, falling under one of the five broader divisions called “Social science”. Jurisprudence, generally defined as the philosophy of law, intersects and interacts with various other Social sciences. The study of such intersection and interaction fosters a rich and multidisciplinary understanding of law’s role in society.
Comparative Analysis
- Sociology and Jurisprudence are deeply interrelated, as the former studies societal structures and behaviours, while the latter examines legal systems and principles. Understanding laws requires insight into the social context in which they operate. Conversely, sociological analysis often relies on legal frameworks to comprehend societal norms, values, and conflicts.
- Psychology and Jurisprudence intersect significantly, as understanding human behaviour is crucial in legal contexts. Psychological insights apprise judicial decisions, witness reliability, and criminal profiling. Additionally, psychological theories help assess intent and competency in legal cases, influencing verdicts and sentencing. This interplay enhances the justice system’s effectiveness and fairness in addressing human actions.
- Anthropology and Jurisprudence intersect by examining how cultural practices shape legal systems. Anthropological insights reveal the diverse ways societies understand justice, rights, and community. This relationship enriches Jurisprudence, as legal frameworks adapt to cultural contexts, fostering inclusivity. By studying human behaviour and societal norms, anthropology enlightens law, ensuring that it resonates with the lived experiences of varied communities.
- Political science analyses the structures, processes, and behaviours that shape governance, while Jurisprudence examines the nature and philosophy of law. Together, they explore how laws influence political systems and how political contexts affect legal principles, fostering a comprehensive understanding of governance and justice.
- History and Jurisprudence are intricately linked, as legal systems evolve through time, reflecting societal values and struggles. Historical events shape laws, while Jurisprudence interprets and preserves these legacies. This symbiotic relationship helps societies learn from past injustices, fostering a more equitable legal framework that addresses contemporary challenges and aspirations.
- Philosophical thought probs into concepts of justice, morality, and the nature of law. Philosophical frameworks provide the foundation for legal theories, prompting critical analysis of ethical dilemmas and societal norms. This dynamic relationship enriches Jurisprudence, encouraging lawmakers to create laws that reflect deeper values, ultimately shaping a just and equitable society.
- Economics and Jurisprudence intersect profoundly, shaping societal structures and individual behaviours. Economic principles are pivotal in forming legal frameworks, influencing policy decisions, and resource allocation. Conversely, legal rules govern economic transactions, ensuring fairness and stability. This dynamic interplay fosters a balanced society, where justice and economic efficiency collaboratively drive progress and enhance overall well-being.
- Ethics and Jurisprudence both explore concepts of justice, morality, and human behavior. Jurisprudence examines the legal framework, while ethics focuses on moral principles guiding individual and societal conduct. Legal systems often reflect ethical standards and ethical considerations can influence law-making and interpretation, ensuring that laws promote justice and reflect societal values.
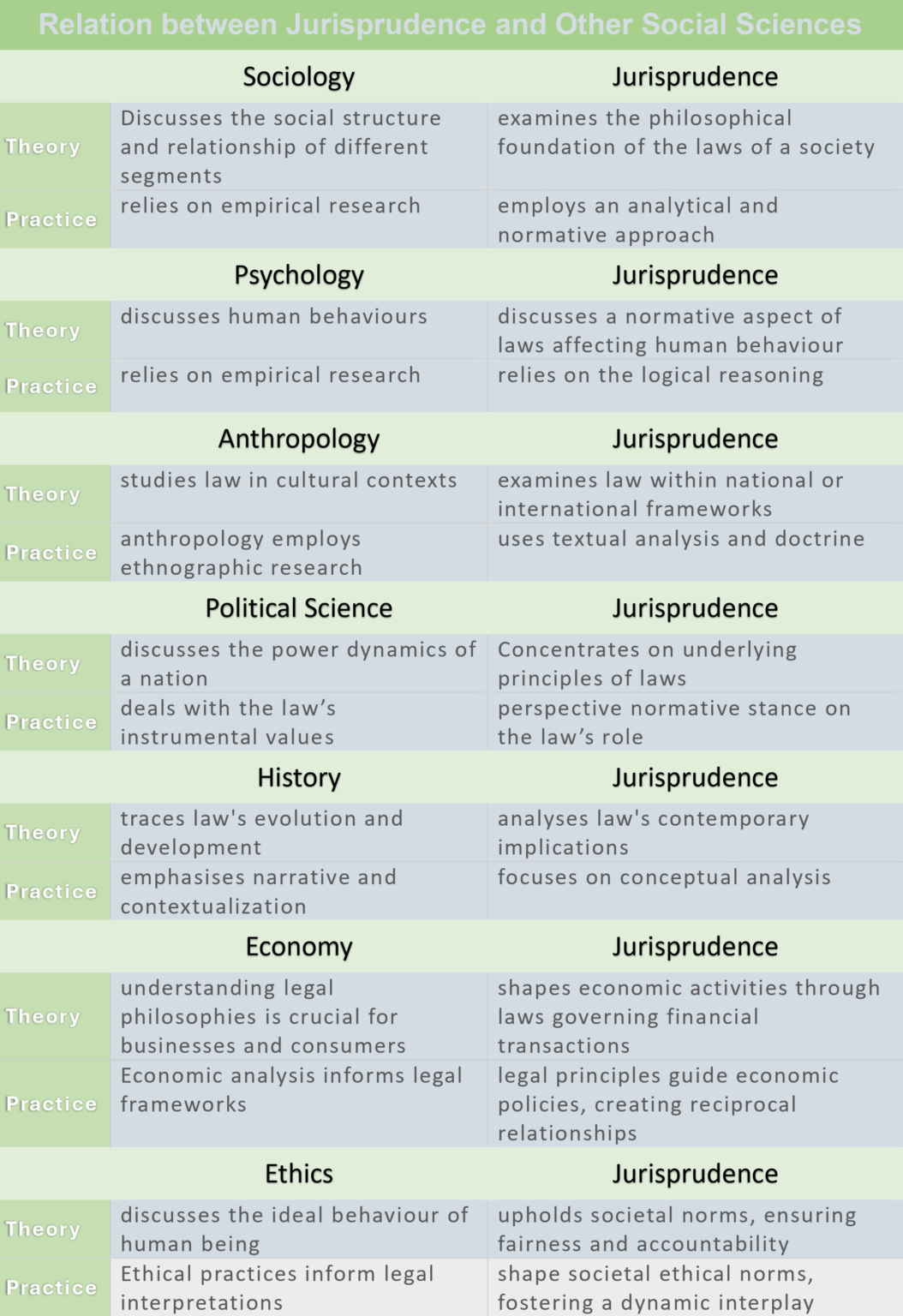
Table Showing Comparison
The table below, highlights the intricate connections between jurisprudence and various social sciences, showcasing how legal principles intersect with sociology, psychology, economics, political science, etc. By illustrating these relationships, we can better understand how law influences and is influenced by, societal structures, behaviours, and economic systems, enriching our grasp of justice and governance.
Conclusion
The interplay between jurisprudence and
various social sciences—such as sociology, psychology, political science,
anthropology, philosophy, history, economics, and ethics—underscores the
multifaceted nature of law. Each discipline offers unique insights that enhance
our understanding of legal systems, revealing how laws reflect societal values,
human behavior, and historical contexts. This interdisciplinary approach not
only deepens our comprehension of jurisprudential concepts but also highlights
the importance of a holistic view in addressing complex legal issues. By
embracing the contributions of these fields, we can foster a richer dialogue
about justice, governance, and the evolving nature of law in society.


